- August 12, 2024
- Digital Marketing, seo
- Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
Table of Contents
Google warns about URL parameter errors that affect crawler inefficiencies, especially on e-commerce sites.
URL parameters can yield infinite URLs, causing crawl inefficiencies. Google is looking into potential remedies, such as new algorithms and better contact with site owners. Google advises that URL parameters pose crawling troubles.
It’s all about how websites include special codes in their web addresses known as URL parameters. According to Google, this can lead to some awkward scenarios for its search robots.
What Are the URL Parameters?
Imagine you are in a large library. Each book has a unique code that indicates where you may locate it. Imagine if that coding changed every time someone glanced at the book. URL parameters will function similarly to web addresses.
URL parameters are specific values added to a URL in order to pass data or affect the behavior of the page being accessed. They come after a question mark (?) in the URL and are commonly used to send information to the server, such as filtering or sorting options, session IDs, or tracking data.
Components of URL parameters
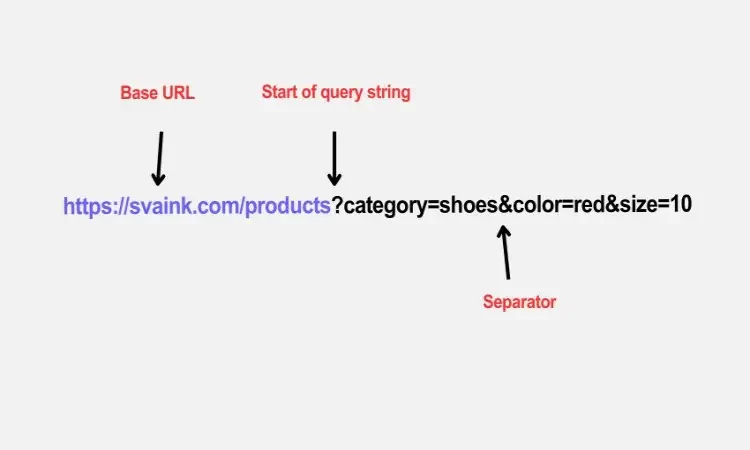
- Base URL: The portion of the URL preceding the parameters. Example: https://example.com/products.
- Parameter String: This is the portion of the URL after the? which contains key-value pairs separated by &. For example:?category=shoes&color=red&size=10.
- Key-Value Pairs: Each parameter has a key and a value separated by a = sign.
Example of a URL containing parameters.
Here is a complete example:
Copy the code: https://example.com/products?category=shoes&color=red&size=10.
- The base URL is https://example.com/products.
- Parameters: category=shoes (product category).
- color=red (filters the products using the color red)
- size=10 (filters goods based on size)
Common Applications of URL Parameters
- Tracking: URL parameters are frequently used to track marketing initiatives. Example: https://example.com?utm_source=newsletter&utm_medium=email.
- Filtering and sorting: Parameters can be used to filter and sort material on a website. Example: https://example.com/products?sort=price_asc.
- Session Management: Parameters can be used to control sessions and monitor user behavior. Example: https://example.com/cart?session_id=12345.
- Pagination: They can assist you browse between pages of content. Example: https://example.com/blog?page=2.
- Dynamic Content: Parameters can alter the content or language of a webpage. Example: https://example.com?lang=fr. (displays the webpage in French)
Impact of URL Parameters on SEO
Why is this an issue?
Google’s search robots, which are similar to super-fast readers, become puzzled by all of these changing addresses. They may assume there are several distinct pages when It’s essentially simply one page with different codes.
Who is most affected?
The main culprits are online shops. They employ these codes to display various colors, sizes, and product categories. Approximately 80% of online retailers use URL parameters in some fashion.
What Can We Do about it?
Google used to provide a dedicated tool to assist with this, but they discontinued it in 2022. They are currently considering innovative solutions to the problem. Several concepts include:
Creating better robots that can recognize when addresses are on the same page.
Asking website owners to clarify how their addresses function
Using special instructions (called robots.txt) to direct the search robots.
Why Should We Care?
This is important whether you have a large store or an online store because:
It will allow Google to find all of your important pages.
It can improve how search engines comprehend your website.
It might improve your website’s visibility in search results.
The Big Picture

If you have a website, you should keep track of how you use these URL parameters. The easier you make things for Google’s robots, the better!
Google warns that URL parameters may cause crawl issues if not properly maintained. URL parameters are the elements of a URL that follow the question mark (?) and are used to send data, such as session IDs, tracking information, or content sorting choices. While they can be beneficial, they may also cause problems such as:
If many URLs with varying parameters point to the same or comparable information, search engines may consider it duplicate content, thereby diluting ranking signals.
Each site has a limited crawl budget that search engines can allocate. If the same content is accessible through multiple URLs with different parameters, crawl money may be wasted on irrelevant pages rather than relevant ones.
Parameters can result in a significant number of URL variations, confusing search engines and making it difficult for them to determine which version should be crawled and ranked.
Excessive parameter usage can result in extremely long URLs that are difficult for search engines to index and users to understand.
Best Practices for managing URL Parameters

To prevent these concerns, adopt the following best practices:
- Canonical tags:
Canonical tags are used to indicate the preferred version of a page when there are many URLs with varying parameters.
- URL Parameter Handling in Google Search Console:
The URL Parameters tool in Google Search Console allows you to specify how Google should handle URL parameters.
- Consistent Parameter Order:
To avoid producing duplicate URLs, ensure that parameters are arranged consistently.
- Minimize Unnecessary Parameters:
Only provide URL parameters that are absolutely necessary.
- Server-Side Rewriting:
If possible, utilize server-side rewriting to simplify URLs and reduce the amount of arguments.
- URL Parameter Management:
Proper URL parameter management ensures that your website is crawled and indexed efficiently, which improves overall SEO performance.
Conclusion
Search engines continue to have difficulty handling URL parameters. Google is working on it, but you should continue to monitor URL structures and utilize tools to guide crawlers.